| |
|

|
|
|
|
| |
|

|
| |
 |
Binary Codes
|
|
|
Binary codes are codes which are represented in binary system with modification from the original ones. Below we will be seeing the following: |
| |
|

|
|
|
- Weighted Binary Systems
- Non Weighted Codes
|
| |
|

|
| |
 |
Weighted Binary Systems
|
|
|
Weighted binary codes are those which obey the positional weighting principles, each position of the number represents a specific weight. The binary counting sequence is an example. |
| |
|

|
|
|
|
Decimal
|
8421
|
2421
|
5211
|
Excess-3
|
|
0
|
0000
|
0000
|
0000
|
0011
|
|
1
|
0001
|
0001
|
0001
|
0100
|
|
2
|
0010
|
0010
|
0011
|
0101
|
|
3
|
0011
|
0011
|
0101
|
0110
|
|
4
|
0100
|
0100
|
0111
|
0111
|
|
5
|
0101
|
1011
|
1000
|
1000
|
|
6
|
0110
|
1100
|
1010
|
1001
|
|
7
|
0111
|
1101
|
1100
|
1010
|
|
8
|
1000
|
1110
|
1110
|
1011
|
|
9
|
1001
|
1111
|
1111
|
1100
|
|
| |
|

|
| |
 |
8421 Code/BCD Code
|
|
|
The BCD (Binary Coded Decimal) is a straight assignment of the binary equivalent. It is possible to assign weights to the binary bits according to their positions. The weights in the BCD code are 8,4,2,1. |
| |
|

|
|
|
Example: The bit assignment 1001, can be seen by its weights to represent the decimal 9 because: |
| |
|

|
|
|
1x8+0x4+0x2+1x1 = 9 |
| |
|

|
| |
 |
2421 Code
|
|
|
This is a weighted code, its weights are 2, 4, 2 and 1. A decimal number is represented in 4-bit form and the total four bits weight is 2 + 4 + 2 + 1 = 9. Hence the 2421 code represents the decimal numbers from 0 to 9. |
| |
|

|
| |
 |
5211 Code
|
|
|
This is a weighted code, its weights are 5, 2, 1 and 1. A decimal number is represented in 4-bit form and the total four bits weight is 5 + 2 + 1 + 1 = 9. Hence the 5211 code represents the decimal numbers from 0 to 9. |
| |
|

|
|
|
|
| |
|

|
| |
 |
Reflective Code
|
|
|
A code is said to be reflective when code for 9 is complement for the code for 0, and so is for 8 and 1 codes, 7 and 2, 6 and 3, 5 and 4. Codes 2421, 5211, and excess-3 are reflective, whereas the 8421 code is not. |
| |
|

|
| |
 |
Sequential Codes
|
|
|
A code is said to be sequential when two subsequent codes, seen as numbers in binary representation, differ by one. This greatly aids mathematical manipulation of data. The 8421 and Excess-3 codes are sequential, whereas the 2421 and 5211 codes are not. |
| |
|

|
| |
 |
Non Weighted Codes
|
|
|
Non weighted codes are codes that are not positionally weighted. That is, each position within the binary number is not assigned a fixed value. |
| |
|

|
| |
 |
Excess-3 Code
|
|
|
Excess-3 is a non weighted code used to express decimal numbers. The code derives its name from the fact that each binary code is the corresponding 8421 code plus 0011(3). |
| |
|

|
|
|
Example: 1000 of 8421 = 1011 in Excess-3 |
| |
|

|
| |
 |
Gray Code
|
|
|
The gray code belongs to a class of codes called minimum change codes, in which only one bit in the code changes when moving from one code to the next. The Gray code is non-weighted code, as the position of bit does not contain any weight. The gray code is a reflective digital code which has the special property that any two subsequent numbers codes differ by only one bit. This is also called a unit-distance code. In digital Gray code has got a special place. |
| |
|

|
|
|
|
Decimal Number
|
Binary Code
|
Gray Code
|
|
0
|
0000
|
0000
|
|
1
|
0001
|
0001
|
|
2
|
0010
|
0011
|
|
3
|
0011
|
0010
|
|
4
|
0100
|
0110
|
|
5
|
0101
|
0111
|
|
6
|
0110
|
0101
|
|
7
|
0111
|
0100
|
|
8
|
1000
|
1100
|
|
9
|
1001
|
1101
|
|
10
|
1010
|
1111
|
|
11
|
1011
|
1110
|
|
12
|
1100
|
1010
|
|
13
|
1101
|
1011
|
|
14
|
1110
|
1001
|
|
15
|
1111
|
1000
|
|
| |
|

|
| |
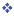 |
Binary to Gray Conversion
|
| |
|

|
|
|
- Gray Code MSB is binary code MSB.
- Gray Code MSB-1 is the XOR of binary code MSB and MSB-1.
- MSB-2 bit of gray code is XOR of MSB-1 and MSB-2 bit of binary code.
- MSB-N bit of gray code is XOR of MSB-N-1 and MSB-N bit of binary code.
|
| |
|

|
| |
|

|
| |
|

|
|
|
|
| |
|

|